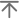
Tubulin is a major cytoskeleton component that has five distinct forms, designated α, β, γ, δ and ε Tubulin. α and β Tubulins form heterodimers which multimerize to form a microtubule filament. There are five β Tubulin isoforms (β1, β2, β3, β4A and β4B) that are expressed in mammalian tissues. β1 and β4 are present throughout the cytosol, β2 is present in the nuclei and nucleoplasm, and β3 is a neuron-specific cytoskeletal protein. γ Tubulin forms the gammasome, which is required for nucleating microtubule filaments at the centrosome. Both δ Tubulin and ε Tubulin are associated with the centrosome. δ Tubulin is a homolog of the Chlamydomonas δ Tubulin Uni3 and is found in association with the centrioles, whereas ε Tubulin localizes to the pericentriolar material. ε Tubulin exhibits a cell cycle-specific pattern of localization; first associating with only the older of the centrosomes in a newly duplicated pair, and later associating with both centrosomes.
1.Weisenberg, R. 1981. Invited review: the role of nucleotide triphosphate in Actin and Tubulin assembly and function. Cell Motil. 1: 485-497.
2. Hoffman, P.N. 1988. Distinct roles of neurofilament and Tubulin gene expression in axonal growth. Ciba Found. Symp. 138: 192-204.
3. Zheng, Y., Jung, M.K. and Oakley, B.R. 1991. g Tubulin is present in Drosophila melanogaster and Homo sapiens and is associated with the centrosome. Cell 65: 817-823.

 010-64814275
010-64814275
 當前位置:
當前位置:




 010-64814275
010-64814275
 010-64814275
010-64814275
 2850669802
2850669802